Introduction
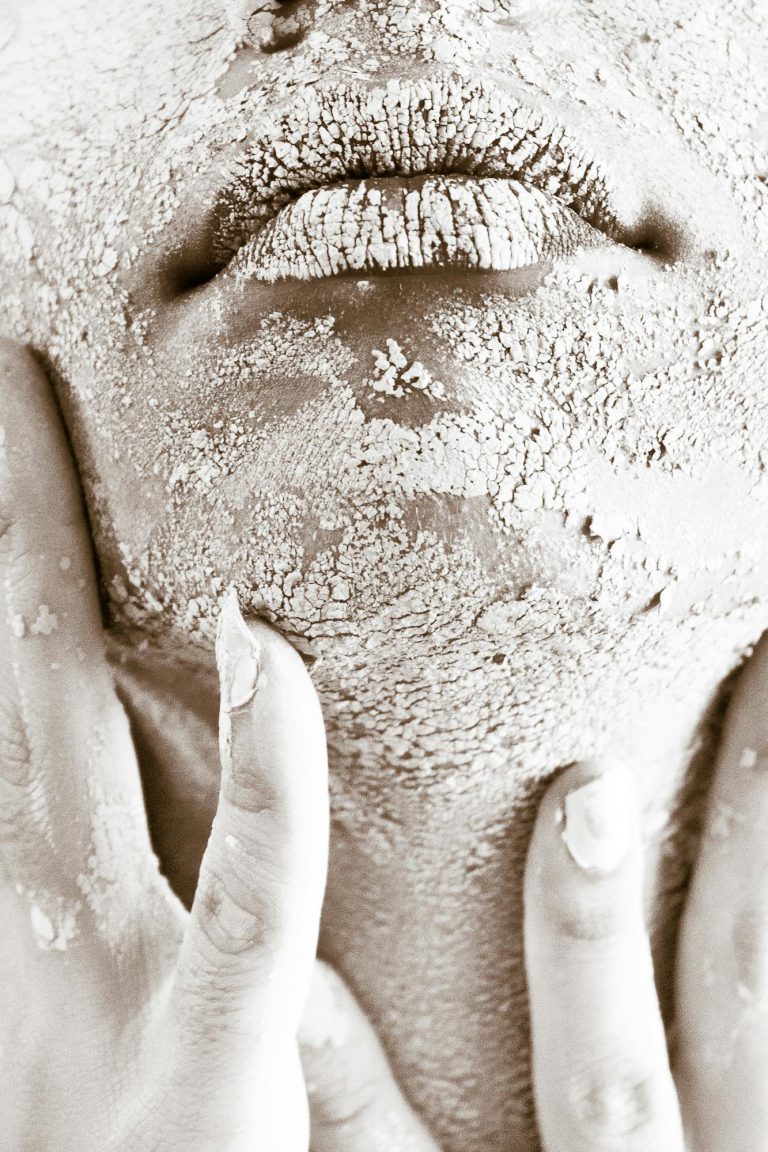
it’s a perfect summer afternoon. You’re stretched out on a blanket in the park, sipping iced tea, soaking up that golden vitamin D… and then, a few hours later, you notice your skin looks less like a healthy glow and more like you’ve gone twelve rounds with a tomato. What happened?
Welcome to the tricky world of photosensitivity—also known as photoallergic dermatitis. It’s not just regular sunburn; it’s your skin throwing a dramatic tantrum because sunlight and certain substances decided to form an unholy alliance. And here’s the kicker: some of the culprits aren’t chemicals from a lab, but beloved plants from your grandmother’s herbal medicine cabinet.
Yes, I’m talking about calendula (marigold), chamomile, and St. John’s wort—those gentle-sounding herbal darlings that, under the wrong conditions, can turn your sunny day into a rashy nightmare.
What Exactly Is Photosensitivity?
Think of photosensitivity as a “sun allergy.” Normally, your skin can handle a fair amount of UV rays before protesting. But when you use or consume certain substances, the sun suddenly becomes that one ex-friend who always ruins the party.
There are two main flavors:
- Phototoxic reaction – Your skin reacts directly to sunlight + substance combo. It’s fast, often painful, and looks suspiciously like a burn.
- Photoallergic reaction – Slower, sneakier, and immune-system-driven. The skin gets inflamed, itchy, and rashy, sometimes hours or even days after exposure.
And here’s the twist: herbs with otherwise wonderful health benefits can push your skin into this overreaction mode.
The Plant Suspects
🌼 Calendula (Marigold)
Calendula tea for sore throats? Calendula cream for scrapes? Lovely! Calendula oil for your skin before a beach day? Not so lovely. The compounds in calendula can make your skin extra sensitive to UV radiation, turning that healing salve into a sunburn starter pack.
Pro tip: Use calendula at night. Let it do its job while you snooze, not while you bake in the sun.
🌿 Chamomile
Chamomile tea before bed is practically a national pastime in some countries. It calms the nerves, eases digestion, and whispers sweet lullabies to your soul. But chamomile applied to skin before sunbathing? It’s like sending an RSVP to the “rash and redness” party.
Chamomile contains furanocoumarins, the compounds responsible for photosensitivity. Ironically, this “gentle” herb can turn quite mischievous under UV rays.
Pro tip: Chamomile baths are for candlelight evenings, not poolside afternoons.
🌞 St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum)
Now here’s the real troublemaker. St. John’s wort is famous for lifting moods and helping with mild depression. But one of its main compounds, hypericin, is practically allergic to the sun. Farmers even report that livestock grazing on this plant develop blistered skin when left in strong sunlight.
For humans, this means two things:
- Drinking St. John’s wort tea before a hike? Risky.
- Using St. John’s wort oil for massage before a tanning session? Downright reckless.
Pro tip: If you’re taking St. John’s wort as a supplement, treat sunscreen like it’s your new religion.
Why Herbs Play This Double Game
Herbs aren’t villains. They didn’t evolve just to ruin your summer Instagram photos. Their photoreactive compounds actually serve as natural defense mechanisms against pests and pathogens. In other words, plants use chemistry the way humans use bug spray. Unfortunately, our skin can get caught in the crossfire.
You might be interested in
How to Stay Safe Without Abandoning Herbal Medicine
- Time it right. Use herbal salves and teas in the evening, not before hitting the beach.
- Check labels. Herbal cosmetics often hide these culprits under flowery names like “soothing floral extract.”
- Sunscreen is non-negotiable. Broad-spectrum SPF is your best shield.
- Know your skin. If you’re pale, sensitive, or prone to allergies, be extra cautious.
- When in doubt, patch test. Apply a small amount of herbal product to your inner arm and expose it to sunlight for 15–30 minutes. If your skin screams back at you, that’s your answer.
Final Thoughts: Respect the Herbs, Respect the Sun
Herbal medicine is wonderful, and these plants have been trusted for centuries. But like any relationship, it’s about knowing boundaries. Calendula, chamomile, and St. John’s wort can be your friends—as long as you don’t invite them to your pool party.
So next time you reach for that “all-natural” cream or brew yourself a calming tea before a sunny outing, remember: the sun and herbs sometimes gang up. And trust me, your skin would prefer not to be caught in the middle.
Hungry for more?
Chinese Medicinal Herbs for Dry Inflamed Skin #chinesemedicine #holistichealth #skincaretips